국제학술지 게재 한국式 명상 <뇌파진동>의 과학적·의학적 효과 연구 논문 [2]
지난 2018년 10월 11일 서울에서 5개국이 참여한 <2018 뇌교육 국제 포럼> 메인 세션에서 발표자로 나선 국제뇌교육종합대학원 양현정 교수는 ‘글로벌 명상 트렌드와 뇌파진동명상에 관한 국제 연구 성과’를 주제로 지난 9년간 국제 학술지에 소개된 12편의 논문을 통해 뇌파진동명상의 효과를 구체적으로 제시해 참석자들의 주목을 받았습니다.
뇌파진동명상의 과학적 연구는 뇌교육 중점 연구기관인 한국뇌과학연구원의 주도로 이뤄졌고, 서울대학교병원, 영국 런던대 등 국내외 공동 연구가 이뤄지면서 2010년부터 국제 저명 학술지에 ‘뇌파진동명상’이라는 이름으로 한국식 명상의 과학적·의학적 효과가 본격적으로 게재되기 시작했습니다.
국제뇌교육협회는 국제 학술지에 게재된 뇌파진동명상에 관한 12편의 논문에 대한 리뷰를 다시 한번 소개합니다.
뇌파진동명상 Brain Wave Vibration meditation
뇌파진동명상(BWV)은 한국 고유 정신문화에 기반한 훈련법으로 동적명상과 정적명상이 혼합된 형태의 뇌교육 명상으로 한국뇌과학연구원이 체계화 했다. 한민족 고유의 선도 단학의 원리를 바탕으로 기체조, 호흡•행공, 명상 단계로 훈련이 진행된다.
7. 산화스트레스 반응과 심리적 증상에 있어서의 뇌파진동 명상의 효과
《Comprehensive Psychiatry》, 2015
서울대학교병원-글로벌사이버대학교
2015년 Comprehensive Psychiatry에 보고된 뇌파진동 명상 연구에서는 이 명상법의 심리적, 내분비적 변화가 조사되었다. 평균 4년간 뇌파진동 명상을 진행해온 그룹 (N=54)과 명상의 경험이 없는 컨트롤 그룹(N=58)을 비교하였다. 혈장 산화질소의 레벨이 측정되어졌고, 스트레스 반응 척도, 긍정적 감정과 부정적 감정 스케일, 우울척도, 불안척도가 측정되었다. 그 결과, 뇌파진동 명상그룹은 컨트롤 그룹에 비해 더 높은 혈장 산화질소 레벨을 보임이 발견되었다. 또한 뇌파진동 명상 그룹은 컨트롤 그룹에 비해 우울지수, 불안지수, 스트레스지수에서 더 낮은 점수를 보였고, 긍정적 감정에서 높은 점수를 보였다. 산화질소는 항상성과 면역반응과 관련한 주요한 세포 시그널링 분자이다. 기존의 연구에서, 혈액에서의 산화질소 레벨이 컨트롤그룹에 비해 고혈압 환자그룹에서 유의미하게 낮음이 보여져왔고, 만성적인 경도의 스트레스가 동맥 산화질소 생산을 약화시킴이 보여져왔다. 따라서, 본 연구에서 명상에 의한 혈장 산화질소 레벨의 증가는, 메커니즘은 아직 불분명하며 더 많은 연구가 필요하나, 심혈관계질병의 예방 및 치료보완에 효과적으로 활용될 수 있음을 시사한다.
.gif)
.gif)
[Abstract]
Objective: Brain Wave Vibration (BWV) training is a simple healing practice, a kind of Mind Body Training. This study was designed to investigate the psycho-endocrine differences between BMV practitioners and naïve controls.
Methods: The experimental group included 54 individuals who had participated in BWV. The control group included 58 subjects who had not participated in formal BWV. Levels of plasma NO, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were measured, and the modified form of the Stress Response Inventory (SRI-MF), the Positive Affect and Negative Affect Scale (PANAS), the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), and the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) were administered.
Results: The BWV group demonstrated significantly higher plasma NO levels (p=0.003), and levels of ROS and SOD did not differ between the two groups. The BWV group showed lower scores in BDI (p=0.009), BAI (p=0.009) and stress level (pb0.001) and higher scores on positive affect (p=0.023) compared with the control group. NO levels were associated with increased positive affect (p = 0.024) only in BWV subjects.
Conclusion: BWV may increase NO, a relaxation-related factor, possibly by improving emotional state.
[출처] ‘The effects of brain wave vibration on oxidative stress response and psychological symptoms’, Comprehensive Psychiatry 60, p.99~104, 2015
8. 유방암 방사선 치료를 받는 여성에게 있어서 뇌파진동 명상이 갖는 불안 감소, 피로 감소 효과 및 전반적인 삶의 질 향상
《Complementary Therapies in Medicine》, 2013
서울아산병원-단월드
2013년 서울 아산 병원에서 수행한 연구에 따르면 유방암 방사선 치료를 받는 여성에게 있어서 뇌파진동 명상이 불안, 피로의 감소와 전반적 삶의 질 향상에 유용하다고 한다. 연구에서는, 뇌파진동 명상이 유방암 방사선 치료를 받는 여성의 불안, 우울, 피로, 삶의 질에 미치는 영향을 알아보기 위해, 유방보존수술을 받은 102명의 여성 유방암 환자를 임의로 균등하게 명상그룹(51명) 또는 컨트롤 그룹(51명)에 배정하여, 뇌파진동 명상그룹은 6주의 방사선 치료 기간 동안 총 12번의 뇌파진동 명상 치료 세션을, 컨트롤 그룹은 기존의 방사선 치료만을 받았다. 그 결과, 뇌파진동 명상그룹은 컨트롤 그룹에 비해 불안, 피로의 감소. 전반적인 삶의 질 향상을 보였다. 본 연구의 결과로, 뇌파진동 명상이 유방암을 가진 여성의 불안, 피로를 감소시키고, 삶의 질, 감정적 능력을 향상시키기 위한, 비침습적인 개입 치료로 사용되어질 수 있음이 시사되었다.
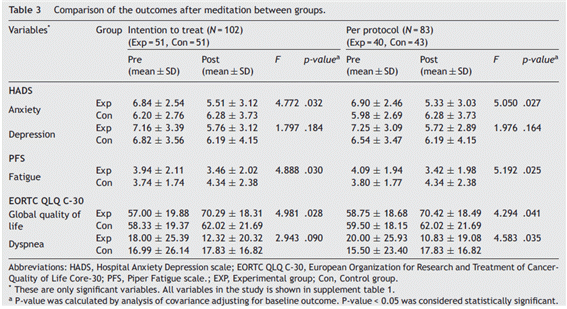
수치가 낮을수록 불안⦁피로가 적고, 수치가 높을수록 삶의 질을 높게 느낌.
[Abstract]
Objective: To investigate the effects of meditation on anxiety, depression, fatigue, and quality of life in women who are receiving radiation therapy for breast cancer.
Design: Randomized, non-program controlled, parallel intervention clinical trial.
Setting: The ASAN Cancer Center located in Seoul, Korea.
Intervention: The subjects of this study included 102 female breast cancer patients who had undergone breast-conserving surgery; these female patients were randomized into equally assigned meditation control groups, with each group consisting of 51 patients. The test group received a total of 12 meditation therapy sessions during their 6-week radiation therapy period, and the control group underwent only a conventional radiation therapy.
Outcome: The tools used to evaluate the effects of meditation were Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale, Revised Piper Fatigue scale, and European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Quality of Life Core-30. The results were analyzed based on the principles of intention-to-treat analysis, and, as a corollary analysis, per-protocol analysis was conducted.
Results: The breast cancer patients who received meditation therapy compared with the nonintervention group saw improvements in reduction of anxiety (p = .032), fatigue (p = .030), and improvement in global quality of life (p = .028).
Conclusions: Based on the results of this study, an affirmation can be made that meditation can be used as a non-invasive intervention treatment for improving fatigue, anxiety, quality of life, and emotional faculties of women with breast cancer
[출처] ‘Effects of meditation on anxiety, depression, fatigue, and quality of life of women undergoing radiation therapy for breast cancer’, Complementary Therapies in Medicine 21, p.379~387, 2013
9. 뇌파진동 명상에 의한 유전적 배경에서 오는 성격적 특성 변화의 가능성
《Psychiatry Investigation》, 2016
서울대학교병원-글로벌사이버대학교
2016년 1월 Psychiatry Investig에서는, BDNF Val66Met다형성에 따른 성격, 행동 활성, 억제시스템에서의 뇌파진동 명상 훈련 효과에 대해 보고하고 있다. 심신운동이 성격, 행동, 감정적 웰빙에 영향을 줄 수 있다는 것이 알려져 있으나 유전적 배경의 차이에 따라 심신운동이 이러한 효과에 어떤 영향을 미치는지 보고된 적은 없다. 이것을 알기 위해, 건강한 피험자 64명, 뇌파진동 명상 피험자 72명이 참가하였고, 성격(외향성, 신경증적 경향, 열린마음)과 행동(행동 활성, 행동 억제) 시스템을 조사하였으며, 모든 피험자에 대하여 유전자 BDNF에서 발현하는 단백질의 66번 아미노산이 발린(V, Val)인지 메티오닌(M, Met)인지에 대해 유전자형을 조사하였다.
연구의 결과, BDNF V/V+V/M그룹에서, 뇌파진동 그룹은 컨트롤 그룹에 비해 외향성 증가, 열린마음의 증가를 보였다. 또한, M/M그룹에서, 뇌파진동 그룹은 컨트롤 그룹에 비해, 외향성의 증가, 신경증적 경향의 감소, 경험에 대한 열린마음의 증가를 보였다. BDNF V/V+V/M 그룹에서, 뇌파진동 그룹은 컨트롤 그룹에 비해 행동억제의 감소를 보였다. M/M그룹에서, 뇌파진동 그룹은 컨트롤 그룹에 비해, 행동활성 중 즐거움 추구가 증가하였고, 행동억제가 감소하였다. 이와 같이 뇌파진동 명상은, 각각의 유전자형에 근거하여 다른 취약성을 보완하면서, BDNF유전적 다형성에 따라 성격 및 행동활성, 억제시스템에 다르게 기여한다는 것이 시사되었다.
[Abstract]
Objective: It has been known that mind-body training (MBT) can affect personality and behavior system as well as emotional well-being, but different effects of MBT on them has not been reported according to BDNF genetic polymorphism.
Methods: Healthy subjects consisted of 64 subjects and the MBT group who practiced meditation regularly consisted of 72 practitioners. Participants completed neuroticism-extraversion-openness (NEO) Five-Factor Inventory and Behavioral Activation System/Behavioral Inhibition System (BAS/BIS) scales. All subjects were genotyped for the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism.
Results: In the same genotypes of the BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met group, MBT group showed the increased Extraversion (p=0.033) and the increased Openness to Experience (p=0.004) compared to the control group. Also, in the same Met/Met carriers, MBT group exhibited the increase of Extraversion (p=0.008), the reduction of Neuroticism (p=0.002), and the increase of Openness to Experience (p=0.008) compared to the control group. In the same genotypes of the BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met group, MBT group showed the decreased BAS-Reward Responsiveness (p=0.016) and the decrease of BIS (p=0.004) compared to the control group. In the BDNF Met/Met group, MBT group increased BAS-Fun Seeking (p=0.045) and decreased BIS (p=0.013) compared to the control group.
Conclusion: MBT would differently contribute to NEO personality and BAS/BIS according to BDNF genetic polymorphism, compensating for different vulnerable traits based on each genotype.
[출처] ‘Effects of mind-body training on personality and behavioral activation and inhibition system according to BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism’, Psychiatry Investigation 13(3), p.333~340, 2016
10. 심신힐링 온라인 뇌파진동 명상 프로그램에 의한 스트레스 감소, 문제해결능력/정서 지능/회복력의 향상
《Plos-one》, 2016
서울대학교병원-글로벌사이버대학교
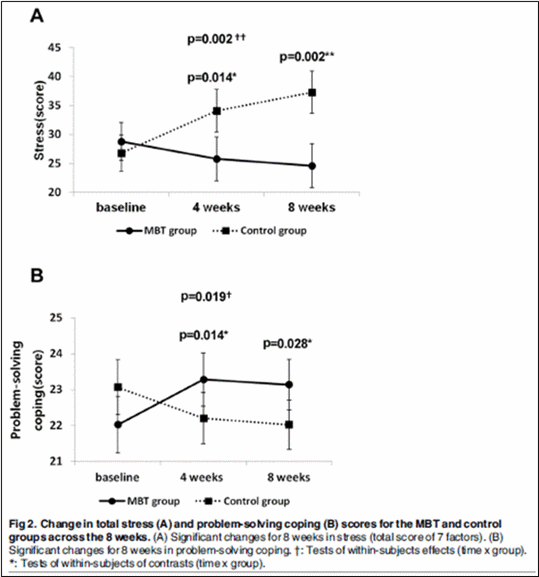
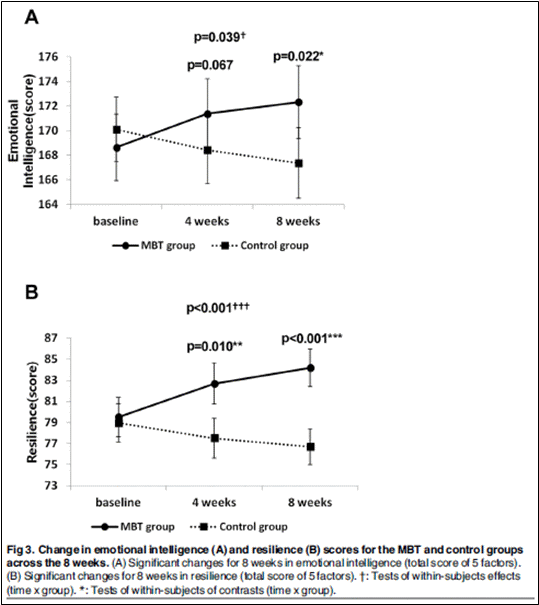
뇌파진동명상은 오프라인만이 아니라 온라인으로도 개발이 되어 그 효과연구가 2016년 Plos One지에 발표되었다. 연구의 목적은 참가자의 스트레스, 분노, 대처전략, 정서지능, 회복력, 긍정적/부정적 감정에 대하여 온라인 뇌파진동 명상 프로그램의 효과를 평가하는 것이다.
시험그룹에는 42명의 건강한 여성이 하루 약 10분씩, 주당 5일, 8주간 참여하였고, 프로그램을 경험하지 않는 컨트롤그룹에는 45명의 건강한 여성이 참여하였다. 참가한 여성의 대부분은 간호사 또는 병원에서 환자를 돌보거나 보조하는 업무를 담당하고 있었다. 프로그램 전과, 개시 4주, 8주 후에 자기보고식 심리학적 설문지가 작성되었다. 온라인 프로그램 그룹과 컨트롤 그룹은 반복측정 분산분석과 Student’s t-test를 사용해 비교되었다.
연구결과, 의미 있는 시간 대비 그룹 상호간의 효과차이가, 스트레스, 대처 전략, 분노, 정서지능, 부정적 감정과 회복력에 대하여 보여졌다.
이 결과는 온라인 뇌파진동명상의 유익한 효과와 컨트롤그룹에 비해 참가자의 심리적 역량에서 의미 있는 향상을 제시한다. 온라인 뇌파진동명상의 효과는 심리학적 측면에서 이전의 오프라인 뇌파진동명상의 효과와 비슷하였다. 온라인 뇌파진동명상의 스트레스와 감정과 관련된 신경과학적 메커니즘이 오프라인 뇌파진동명상과 유사한지에 대하여는 심화된 연구가 필요하다.
[Abstract]
The goal of this study was to evaluate the effects of an online mind-body training (MBT) program on participants’ stress, anger, coping strategies, emotional intelligence, resilience, and positive and negative affect. Forty-two healthy women participated in an online MBT program for approximately 8–10 minutes a day for 8 weeks; a control group of 45 healthy women did not participate in the program. Self-report psychological questionnaires were administered before the beginning of the program and at 4 and 8 weeks following its onset. Data from the MBT group and the control group were compared using repeated measures ANOVA and Student’s t-tests. Significant time x group interaction effects were found with respect to stress, coping strategies, anger, emotional intelligence, negative affect and resilience. These results demonstrate beneficial effects of the online MBT program and significant improvements in the psychological capabilities of participants compared with the control group. The effects of online MBT program were similar with those of the previous offline MBT in psychological aspects, suggesting further studies for neuroscientific evidence related stress and emotion of online MBT effects.
[출처] ‘The effects of an online mind-body training program on stress, coping strategies, emotional intelligence, resilience and psychological state’, Plos-one 11(8), e0159841, 2016
11. 뇌파진동명상이 사이토카인에 미치는 영향 및 카테콜아민과의 상호작용연구
《Psychiatry Investigation》 2017
서울대학교병원-글로벌사이버대학교
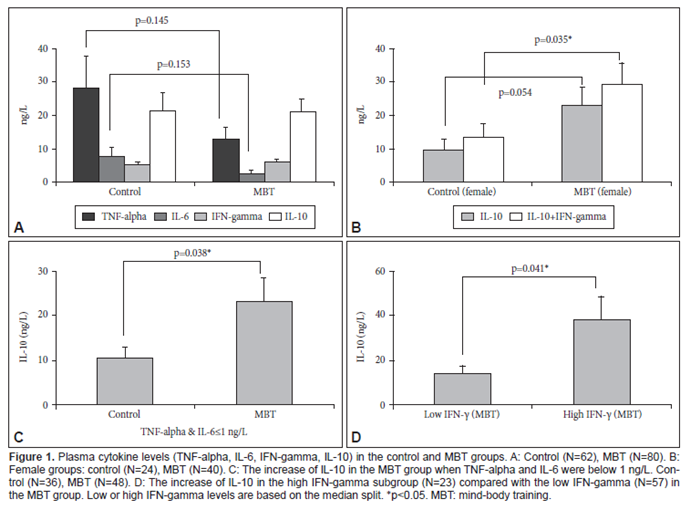
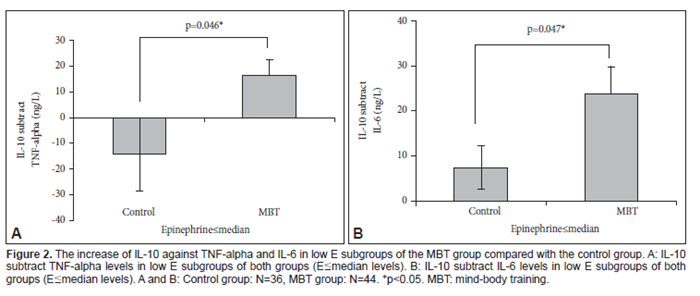
2017년 Psychiatry Investig지에 보고된 연구에 따르면 뇌파진동 명상이 면역계에 변화를 유도한다고 한다. 연구에서는 혈장 사이토카인과 이것의 카테콜아민과의 상관관계를 밝히기 위해 뇌파진동명상을 수행하는 80명의 피험자와 62명의 건강인의 혈장 카테콜아민(노르에피네프린, 에피네프린, 도파민)과 사이토카인(TNF-alpha, IL-6, IFN-gamma, IL-10) 을 측정하였다. 뇌파진동 명상 수행자중 여성에서 컨트롤에 비해 IL-10+IFN-gamma 값에서 유의미한 증가가 발견되었다. 또한, 뇌파진동명상그룹에서 TNF-alpha와 IL-6가 거의 없는 상태(1ng/L보다 낮은 상태)에서 IL-10(항염증성 사이토카인)의 유의미한 증가가 발견되었다. 뇌파진동명상 그룹에서는, IL-10과 노르에피네프린/에피네프린 비율에 유의미한 긍정적인 상관관계가 발견되었고, 또한 IL-10과 도파민/에피네프린 비율간의 유의미한 긍정적 상관관계가 발견되었다. 반면, 컨트롤 그룹에서는 이러한 상관관계가 발견되지 않았다.
이러한 연구결과에 따라 저자들은 뇌파진동명상이 스트레스 반응을 조절하여, 특히 염증촉진성 사이토카인이나 에피네프린이 줄어든 상태에서 IL-10을 증가시키며, 이것은 신경계와 면역계간 유효하고 긍정적인 상호작용에 기여하는 것 같다고 해석하였다.
[Abstract]
Objective: Mind-body training(MBT) may control reactions to stress and regulate the nervous and immune systems. The present study was designed to assess the effects of MBT on plasma cytokines and their interactions with catecholamines.
Methods: The study group consisted of 80 subjects who practice MBT and a control group of 62 healthy subjects. Plasma catecholamine(norepinephrine, NE; epinephrine, E; and dopamine, DA) and cytokin (TNF-alpha, IL-6, IFN-gamma, and IL-10) levels were measured, and the differences between the MBT and control groups and the interactions of cytokines with catecholamines were investigated.
Results: A significant increase in IL-10+IFN-gamma was found in females of the MBT group compared with controls. Also, a significant increase of IL-10(anti-inflammatory cytokine) in the MBT group was shown in a specific condition in which TNF-alpha and IL-6(pro-inflammatory cytokines) are almost absent (≤1 ng/L) compared with controls. In the MBT group, significant positive correlations were found between IL-10 and the NE/E ratio and between IL-10 and the DA/E ratio, whereas the control group did not show any such correlations.
Conclusion: MBT may increase IL-10, under specific conditions such as a decrease of pro-inflammatory cytokines or E, which may regulate the stress response and possibly contribute to effective and beneficial interactions between the nervous and immune systems.
[출처] ‘Effects of mind-body training on cytokines and their interactions with catecholamines’, Psychiatry Investigation 14(4), p.483-490, 2017
12. 뇌파진동 명상 수행자와 비수행자의 뇌섬엽에서의 기능적 연결성의 차이
《JOURNAL MINDFULNESS》 2018
서울대학교병원-성균관대학교 의과대학-한국뇌과학연구원
2018년 3월 Mindfulness저널에 서울대 병원, 성균관의대, 한국뇌과학연구원에서 공동수행한 뇌파진동 명상에 의한 뇌섬엽의 기능적 연결성의 변화에 대한 연구결과가 발표되었다. 본 연구에서는, 휴식상태에서 뇌섬엽과 다른 뇌부위의 기능적 연결성이, 명상에 의해 어떻게 변화하는지 조사하기 위해 행하여졌다. 명상그룹 35명과 비명상 그룹 33명에 대하여 4.68분간 자기공명영상을 이용한 휴식상태에서의 기능적 스캐닝을 행하였다. 명상수행자들은 시상, 미상핵, 중전두회, 상측두회에서, 뇌섬엽과 관련된 기능적 연결성이 훨씬 더 증가하여 있었다. 컨트롤 피험자들은 해마방회에서 후방 뇌섬엽과의 기능적 연결성이 더 증가하여 있었다. 연구자들은 뇌파진동명상수행이 집중된 주의, 집행 조절, 감정 인식 및 조절과 관련된 뇌영역에서 기능적 차이와 관련되어있을지 모른다고 추정한다.
.png)
[Abstract]
The majority of meditation involves focusing attention on internal events or sensations and becoming aware of emotions. The insula cortex, through a functional connection with the prefrontal cortex and other brain regions, plays a key role in integrating external sensory information with internal bodily state signals and emotional awareness. The purpose of this exploratory study was to examine the resting-state functional connectivity of the insula with other brain regions in meditation practitioners and control subjects. Thirty-five Brain Wave Vibration meditation practitioners and 33 controls without meditation experience were included in this study. All subjects underwent 4.68-min resting-state functional scanning runs using magnetic resonance imaging. The anterior and posterior insulae were chosen as seed regions for the functional connectivity map. Meditation practitioners showed significantly greater insula-related functional connectivity in the thalamus, caudate, middle frontal gyrus, and superior temporal gyrus than did controls. Control subjects demonstrated greater functional connectivity with the posterior insula in the parahippocampal gyrus. Our findings suggest that the practice of Brain Wave Vibration meditation may be associated with functional differences in regions related to focused attention, executive control, and emotional awareness and regulation.
[출처] ‘Differences in functional connectivity of the insula between brain wave vibration in meditators and non-meditators’, Journal Mindfulness, 2018

